 |
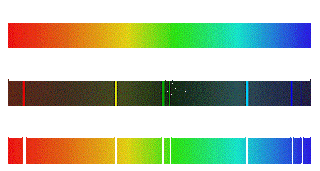
| Spectra |
When the electromagnetic radiation passing through a prism or divided grille, and a set of lines, different wavelengths. This is called the spectrum. The scientific word was first used in the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated by a prism, but it is applied by analogy to many fields of optics. The different spectrum of light through a prism, a solid or liquid, clear, or created from glass which glows compression / uncompressed. When using more modern spectrum is a common denominator between the two extremes at each end.
The spectrum extends to other waves such as sound waves to be measured can be considered as a function of frequency. The absorption spectroscopy technique which measures the effect of the beam before and after the interaction with the sample for comparison. A continuous spectrum of the heat, close, while generating an absorption spectrum of the light of the results of something hot, through a dense cloud cooling, less dense gas. This is the type of spectrum produced by the sun, because the material is actually very dense and hot sun radiates energy in the form of light that brings out a cooler climate.
Three basic type of spectra are:-
1. Line spctrum: This form is due to the absorption or emission of waves by atoms, for example, the dark lines in the spectrum of the Sun absorption lines because of the presence of helium element.
2. Band spectrum: Instead, a broader spectrum of one line. Emssion consists of waves or molecules absorb.
3. Continuous spectrum: The spectrum is continuous, uninterrupted like a ghost. It color.eg continuum emergency tones, so sweet, a little "dark. The problem caused by a specific mechanism. For example, the solar spectrum for the thermal emission. It may be the synchrotron emission (eg. , emission of pulsars), etc.
For Information About Spectroscopy Book Check:- http://spectroscopybook.blogspot.com/
For Information About Operating System (OS) Book Check:- http://operatingsystembook.blogspot.com
Check Labels For more Similar Jobs:-

